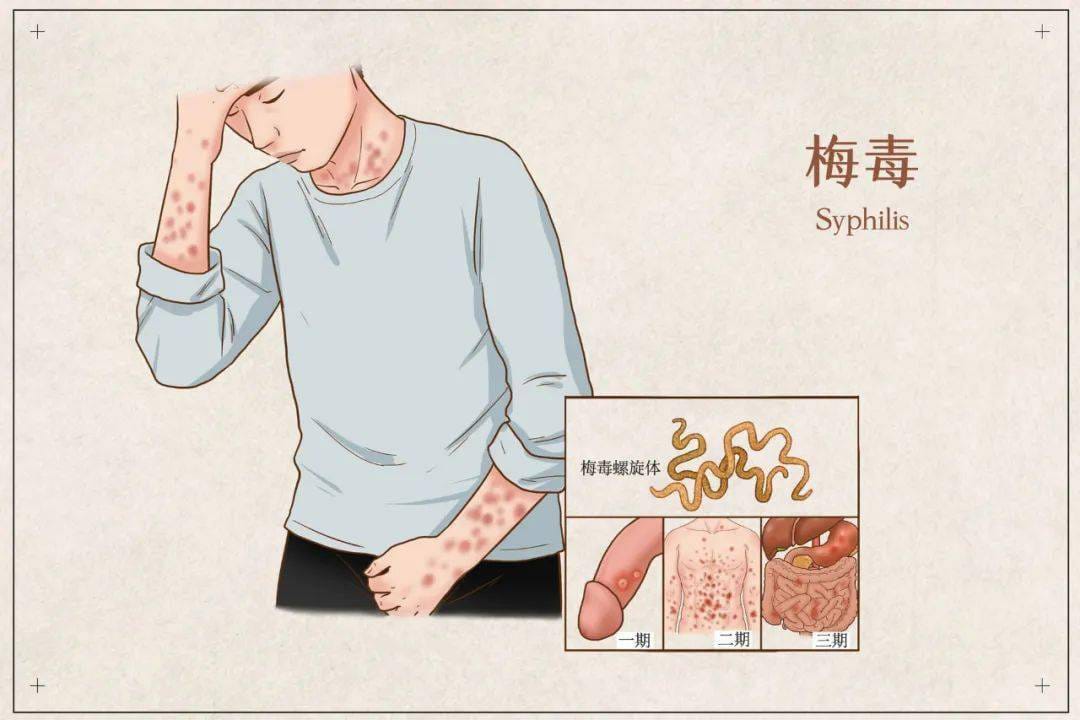
Transmission of Syphilis: How Syphilis Spreads and Prevention Strategies
Syphilis is a serious bacterial infection caused by Treponema pallidum that remains a significant global health concern. Understanding exactly how syphilis transmits is crucial for effective prevention and control of this sexually transmitted infection (STI). Often called "the great imitator" due to its varied symptoms, syphilis has specific transmission patterns that everyone should understand to protect their sexual health. This comprehensive guide explores all aspects of syphilis transmission, from common routes to rare cases, and provides evidence-based prevention strategies.
How Syphilis is Primarily Transmitted
Direct Contact with Infectious Sores
The primary transmission method involves direct contact with a syphilis sore (called a chancre) during sexual activity. These sores contain the bacteria that cause syphilis.
Key Facts:
- Sores can be hidden: They may occur inside the vagina, anus, rectum, or mouth
- Painless nature: Chancres are typically painless, so people may not know they have them
- Multiple locations: Sores can appear on genitals, lips, tongue, or other contact areas
- Infectious period: Sores are most infectious during primary and secondary stages
Primary Transmission Routes
Sexual Transmission
Most syphilis cases are transmitted through sexual contact:
Vaginal Sex:
- Direct contact between genital sores and vaginal mucosa
- Transmission can occur from male to female and female to male
- Estimated transmission risk: 30-60% per exposure with active lesions
Anal Sex:
- Higher risk due to tissue vulnerability and potential for microscopic tears
- Affects both receptive and insertive partners
- Particularly concerning for men who have sex with men (MSM)
Oral Sex:
- Transmission through contact with genital sores and oral mucosa
- Often underestimated transmission route
- Can cause primary sores in the mouth or throat
Mother-to-Child Transmission (Congenital Syphilis)
Vertical transmission occurs when an infected pregnant person passes the infection to their baby:
Transmission Timing:
- During pregnancy: Across the placenta (most common)
- During delivery: Contact with infectious lesions in birth canal
- Rarely through breastfeeding: If breast lesions are present
Impact on Pregnancy:
- 50-80% transmission rate without treatment
- Can cause stillbirth, neonatal death, or severe disability
- Preventable with proper prenatal screening and treatment
Factors Influencing Transmission Risk
Biological Factors
Stage of Infection:
- Primary and secondary stages: Highly contagious due to visible sores and skin lesions
- Early latent stage: Still potentially infectious, especially during the first year
- Late latent and tertiary stages: Generally not contagious through sexual contact
Viral Load in Sores:
- Higher bacterial concentration increases transmission likelihood
- Fresh sores typically have higher bacterial loads
Behavioral and Environmental Factors
Sexual Practices:
- Unprotected sex significantly increases risk
- Multiple sexual partners elevates exposure risk
- Substance use may impair judgment about protection use
Healthcare Access:
- Limited access to testing and treatment increases community transmission
- Stigma may prevent people from seeking care
Less Common Transmission Routes
Blood Transfusion
Extremely rare in modern healthcare due to:
- Routine blood donor screening
- Laboratory testing of all donated blood
- Bacteria survival limitations in stored blood
Direct Non-Sexual Contact
Rare but possible in specific circumstances:
- Direct contact with active lesions during non-sexual caregiving
- Accidental inoculation among healthcare workers
- Sharing of contaminated personal items (theoretically possible but uncommon)
What Does NOT Transmit Syphilis
Understanding what doesn't spread syphilis is equally important for reducing stigma:
No Risk Activities:
- Casual contact: Hugging, holding hands, sharing meals
- Environmental surfaces: Toilet seats, swimming pools, hot tubs
- Shared objects: Utensils, clothing, towels (unless contaminated with fresh sore fluid)
- Airborne transmission: Coughing, sneezing, breathing same air
Prevention Strategies
Proven Prevention Methods
Barrier Protection:
- Consistent condom use: Reduces but doesn't eliminate risk
- Dental dams: For oral-vaginal or oral-anal contact
- Proper lubrication: Reduces tissue trauma during sex
Behavioral Strategies:
- Mutual monogamy with tested partner
- Regular STI testing for sexually active individuals
- Open communication with partners about sexual health
- Reducing number of sexual partners
High-Risk Populations
Certain groups face increased syphilis transmission risk:
Key Populations:
- Men who have sex with men (MSM)
- People living with HIV
- Commercial sex workers
- Young adults (ages 20-35)
- People with multiple sexual partners
- Individuals in correctional facilities
- People with substance use disorders
11/F, 168 Queen’s Road Central, Central
(7 min from Central MTR Exit D2 /
2 min from Sheung Wan MTR Exit E2)
Hourly Parking Nearby : The Center, Grand Millennium Plaza
Mon-Fri : 9:45a.m. – 1:45p.m. ;
3:00p.m. – 6:10p.m.
Sat : 9:45a.m. – 1:15p.m.
Sun and Public Holiday: Close
By Appointment Only

