Syphilis Symptoms in Men & Women: Hong Kong Complete Guide
Understanding Syphilis in Hong Kong
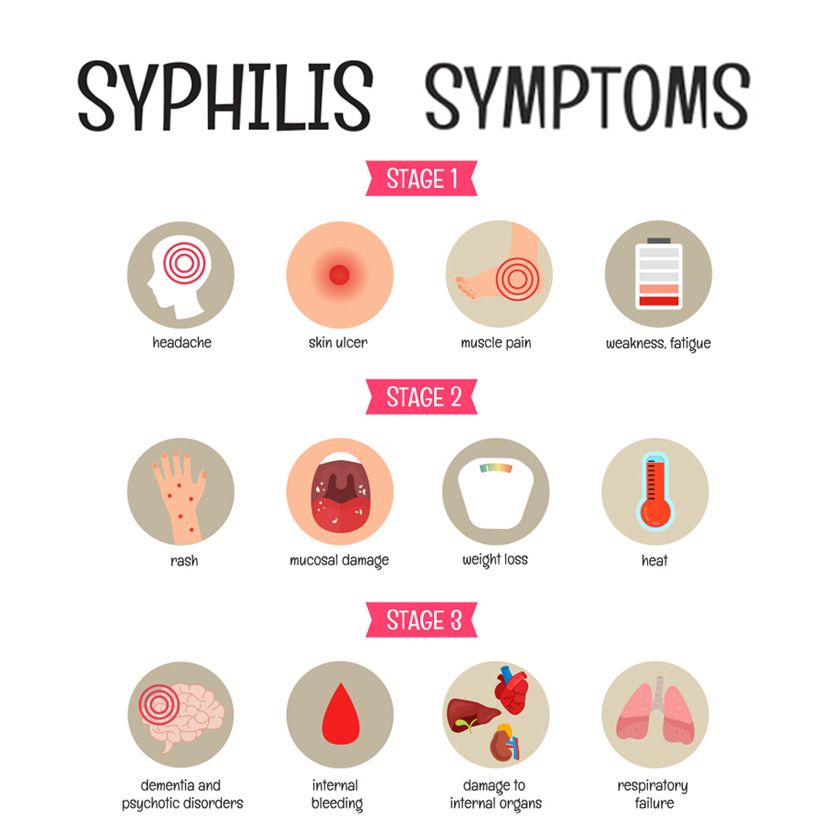
Syphilis is a serious bacterial infection caused by Treponema pallidum that remains a significant public health concern in Hong Kong. According to the Centre for Health Protection, Hong Kong has experienced a concerning increase in syphilis cases in recent years, with reported cases rising by 25% between 2018 and 2022. The infection progresses through distinct stages and can cause severe health complications if left untreated. Many infected individuals experience no noticeable symptoms in the early stages, making regular testing essential for sexually active individuals in Hong Kong.
The Four Stages of Syphilis and Their Symptoms
Primary Syphilis (3-90 days after exposure)
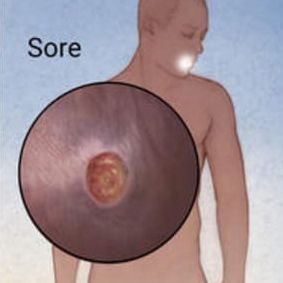
- The appearance of one (or sometimes, multiple) round, painless syphilitic sore(s) (known as chancre) at the location where the bacteria entered the body, which could be the penis, vagina, anus or mouth.
- The chancre can persist up to 3-6 weeks and heal even if you received no treatment.
- Without treatment, the disease will progress to the secondary stage.
Secondary Syphilis (4-10 weeks after chancre appears)
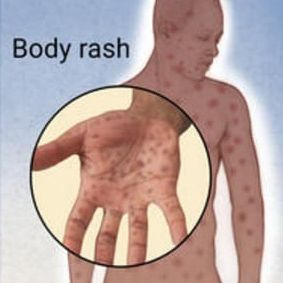
- The development of fever, swollen lymph nodes in the neck and genitals, sore throat, headache, joint pain, muscle aches, tiredness, and skin rash characteristically affecting the palms of hands and soles of feet which is usually not itchy.
- The development of a raised, white/grey lesion (condyloma lata) in warm and moist body parts such as the genitals, armpits and mouth.
- These symptoms will eventually disappear even if you received no treatment.
- Without treatment, the disease will progress to the latent stage.
Syphilis - Latent stage
- During this “hidden” stage, untreated individuals remain infected for years despite the lack of visible signs or symptoms.
- Without treatment, about 15-30% of patients with syphilis will develop tertiary syphilis.
Tertiary Syphilis (10-30 years after initial infection)
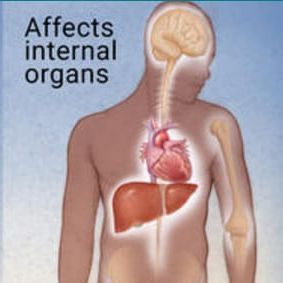
- Tertiary syphilis is a serious, and sometimes life-threatening condition that could occur 30 years after your initial untreated infection.
- It usually involves damage to multiple organs, including the brain, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, joints and the nervous system.
Gender-Specific Symptoms
Symptoms More Common in Men:
- Penile chancres (primary stage)
- Rectal sores (men who have sex with men)
- Urethral discharge (rare)
- Testicular swelling
Symptoms More Common in Women:
- Cervical or vaginal chancres (often unnoticed)
- Vulvar lesions
- Increased risk of transmission to babies during pregnancy
- Symptoms often missed due to internal location
Congenital Syphilis:
- Transmission from mother to baby during pregnancy
- Stillbirth or neonatal death
- Developmental delays in children
- Tooth abnormalities (Hutchinson's teeth)
- Bone deformities
- Vision and hearing loss
Syphilis Testing in Hong Kong
Recommended Testing For:
- All sexually active individuals
- Pregnant women (mandatory screening in Hong Kong)
- Men who have sex with men
- People with multiple partners
- Those experiencing any symptoms
Testing Methods Available:
- Blood tests (VDRL, RPR, TPHA, TPPA)
- Direct detection from chancre fluid (dark-field microscopy)
- Cerebrospinal fluid testing for neurosyphilis
If you suspect or discover any of the above symptoms of syphilis, get a syphilis test as soon as possible for treatment.
- Syphilis (TP) Antibody Test - $250
- Syphilis RPR Test - $150
- Basic STD Screening, HIV, Syphilis, Herpes
Neurosyphilis
During any stages of syphilis infection, the untreated infection can spread and damage the brain and eyes resulting in neurosyphilis and ocular syphilis, which the symptoms include: Headache, Sudden change in behavior and mental status, Meningitis, Problem with muscle movement and co-ordination, Numbness or paralysis, Hearing problems, Visual problems, including blindness*.
* REF: https://www.paho.org/en/topics/sexually-transmitted-infections/syphilis
Syphilis Treatment
Syphilis can be controlled as long as you take antibiotics and complete the full course of syphilis in stage 1 or 2. You should have a blood test after treatment to ensure recovery. You and your sexual partner should avoid sexual contact and wait until 2 weeks after completing the course of treatment before returning to sex. The course of antibiotics for tertiary syphilis may be longer. Whether your sexual partner needs treatment depends on the exposure and the period of infection, please discuss this with your doctor.
Complications of Untreated Syphilis
Neurological Complications:
- Stroke and meningitis
- Dementia and memory loss
- Loss of pain sensation
- Vision loss and hearing impairment
- Sexual dysfunction
Cardiovascular Complications:
- Aortic aneurysm and inflammation
- Heart valve damage
- Blood vessel inflammation
Other Severe Complications:
- Organ failure (liver, kidney)
- Bone destruction
- Skin and tissue damage (gummas)
- Increased HIV transmission risk
(Text Only)

