
Introduction: HIV Treatment Today
The HIV virus cannot be eliminated by the body, therefore once infected, it results in lifelong infection.
There is currently no cure for HIV, but HIV regimen (usually with 3 HIV medicines from 2 different classes combined into one pill taken once a day) known as antiretroviral therapy (ART) is available to suppress HIV replication to undetectable level in order to prevent damage to the immune system, lowers the risk of disease progression to AIDS and transmission to others. HIV infection is no longer considered a death sentence, it is a chronic but manageable illness. With effective treatment, people with HIV can live a long and healthy life.
Understanding Antiretroviral Therapy (ART)
What is ART?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) involves using a combination of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medications every day as prescribed by their healthcare provider.
How ART Works:
- Suppresses viral replication: Prevents HIV from multiplying
- Increases CD4 cell count: Helps rebuild the immune system
- Reduces viral load: Can achieve undetectable status
- Prevents disease progression: Reduces risk of opportunistic infections
- Prevents HIV transmission: Undetectable = Untransmittable (U=U)
Current HIV Treatment Guidelines
When to Start Treatment
Current guidelines recommend starting ART:
- Immediately after diagnosis regardless of CD4 count
- As soon as possible after HIV diagnosis
- During acute HIV infection for better long-term outcomes
Treatment Goals
- Maximal and durable suppression of viral load
- Restoration and preservation of immunological function
- Improved quality of life
- **Reduction of HIV-related morbidity and mortality
- Prevention of HIV transmission
HIV Medication in HK
There are several classes of HIV medicine (REF5), each targeting a different pathway in the HIV replication cycle, which includes:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) – Block reverse transcriptase
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) – Bind to reverse transcriptase
- Protease inhibitors (PIs) – Block protease
- Fusion inhibitors – Block HIV from entering CD4 cells
- CCR5 antagonists – Block CCR5 co-receptors
- Integrase strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) – Block integrase
- Attachment inhibitors – Bind to gp120 protein
- Post-attachment inhibitors – Block CD4 receptors
- Pharmacokinetic enhancers – Increase the effectiveness of HIV medicine
HIV replication cycle.
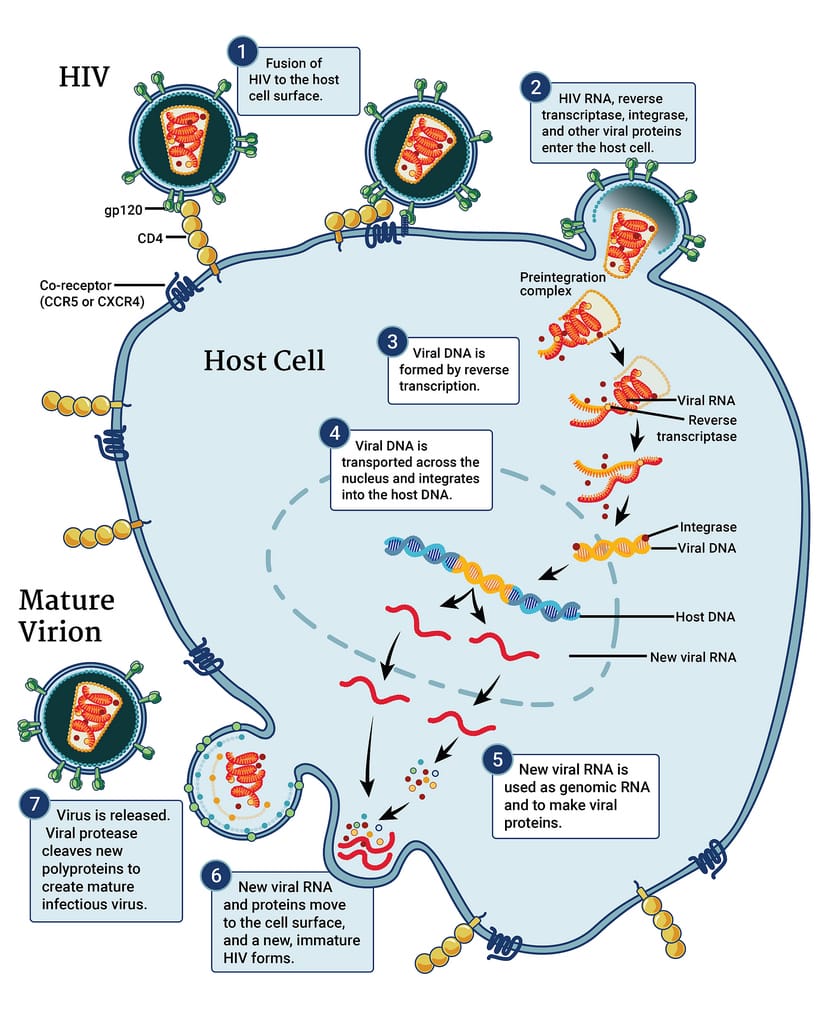
Credit: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/hiv-replication-cycle
Undetectable = Untransmittable (U=U)
The PARTNER (Partners of People on ART – A New Evaluation of the risks) study and the Opposite Attract study were carried out to assess the risk of HIV transmission to the HIV-negative partner from their HIV-positive partner on ART with undetectable HIV viral load. The results show that none of the HIV-negative partners contracted HIV from their HIV-positive partners despite regular unprotected (condomless) sex. However, not everyone on ART can achieve and maintain an undetectable viral load. So, it is crucial for people living with HIV to take their medicine every day and monitor their viral load regularly.
Managing Side Effects and Complications
Common Side Effects:
- Initial side effects: Nausea, headache, dizziness, diarrhea (often temporary)
- Long-term considerations: Bone density, kidney function, cardiovascular health
- Metabolic changes: Lipid abnormalities, insulin resistance
Management Strategies:
- Symptom-specific treatments
- Timing adjustments (taking with food or at bedtime)
- Medication switches when necessary
- Supportive care and lifestyle modifications
Special Considerations in HIV Treatment
Treatment in Special Populations
- Pregnancy: ART to prevent mother-to-child transmission
- Children and adolescents: Age-appropriate formulations and dosing
- Older adults: Managing comorbidities and polypharmacy
- Co-infections: TB, hepatitis B and C management
- Renal or hepatic impairment: Adjusted regimens
Drug Interactions
- Common interactions: With other medications, supplements, and recreational drugs
- Important to discuss: All medications with healthcare providers
- Regular review: Of complete medication list
(Text Only)

