
Introduction: Understanding HIV Transmission Risks
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) transmission risk varies significantly depending on the type of exposure, viral load, and other biological factors. Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions about sexual health and prevention strategies. This comprehensive guide examines the transmission risks associated with different sexual activities, based on the latest scientific evidence and public health data.
HIV Transmission Basics
HIV is transmitted through certain body fluids, including:
- Blood
- Semen
- Pre-seminal fluid
- Rectal fluids
- Vaginal fluids
- Breast milk
The virus must enter the bloodstream to cause infection, which can occur through mucous membranes (found in the rectum, vagina, penis, and mouth) or through breaks in the skin.
HIV can be transmitted:
Most commonly (High Risk):
- By mucosal exposure to infected bodily fluids, including blood, semen, pre-ejaculate, vaginal fluid and rectal fluid, usually through unprotected sexual activity
- By direct exposure to infected blood, usually through sharing needles with infected individuals
Less commonly (Low Risk):
- From infected mother to baby during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. The use of HIV medication during pregnancy can effectively reduce the risk of mother-to-baby transmission to less than 1%.
- Accidental needlestick or sharp injuries, mostly among healthcare professionals. The use of post-exposure prophylaxis can reduce the risk of infection.
Unlikely but possible:
- The risk of transmission through oral sex is generally low, but the risk is increased if cuts, ulcers/open sores or gum disease is present
The HIV virus cannot enter intact (unbroken) skin, so, HIV CANNOT be transmitted by:
- Water
- Air
- Insect bites (e.g. by mosquito or ticks)
- Sweat, tears or saliva that does not contain blood of an infected person
- Sexual activities that do not involve exchange of bodily fluids, e.g. touching
- Social activities such as hugging, shaking hands, closed-mouth kissing, toilets seats, swimming pools, telephones, sharing food or eating utensils
Risk of HIV transmission per exposure from a known HIV-positive individual not on ART.
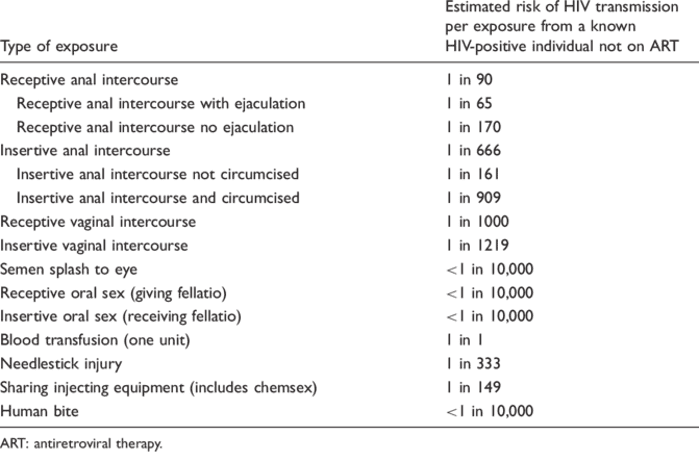
Source: Cresswell, F., Waters, L., Briggs, E., Fox, J., Harbottle, J., Hawkins, D., ... & Fisher, M. (2016). UK guideline for the use of HIV post-exposure prophylaxis following sexual exposure, 2015. International journal of STD & AIDS, 27(9), 713-738.
The Power of HIV Prevention
HIV can be prevented by using condom correctly and persistently during sex and avoid sharing needles with others. The use of HIV medication by infected mothers during pregnancy can reduce the risk of transmission to their babies. In addition, breastfeeding should be avoided by mothers with HIV to prevent transmission through breastmilk.
Undetectable = Untransmittable (U=U)
People with HIV who maintain an undetectable viral load through effective treatment cannot sexually transmit HIV. This is the most effective prevention strategy for serodifferent couples.
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP)
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is a method to prevent HIV infection for people who are HIV-negative to take anti-retroviral medication to reduce the risk of infection if later exposed to the virus, e.g. to engage in sexual activity with a person who is HIV-positive. See PrEP.
- Daily oral PrEP: Reduces risk by approximately 99% when taken consistently
- Event-driven PrEP: Effective for anal sex, less studied for vaginal sex
- Injectable PrEP: Long-acting option with high efficacy
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) is a treatment consists of 28 days of anti-retroviral medication prescribed by doctor to prevent HIV infection after possible exposure to HIV, e.g. after unprotected sex. See PEP.
- Emergency prevention: Must be started within 72 hours of exposure
- 28-day regimen: Reduces infection risk by approximately 80%
- Not for regular use: Intended for emergency situations only
(Text Only)

