Symptoms of Candidiasis in Women and Men: Recognising the Signs

Have you noticed an unusual, itchy rash in a skin fold, discomfort in your intimate areas, or white patches in your mouth? These could be signs of a candidiasis, a common fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida yeasts. While it can affect anyone, the symptoms often differ between women and men, and recognising them is the first step to effective treatment. For residents of Hong Kong, where the hot and humid climate can create an ideal environment for fungal growth, understanding these signs is especially important.
This guide provides a clear, in-depth look at the symptoms of various candidiasis infections, helping you identify when to seek advice from a Hong Kong doctor or clinic.
What is Candidiasis?
Candidiasis is an infection caused by yeasts from the Candida family, most commonly Candida albicans. These yeasts normally live in small, harmless amounts on our skin, in the mouth, digestive tract, and vagina. Problems arise when something disrupts the body's natural balance, allowing the yeast to overgrow. Common triggers include antibiotic use, a weakened immune system, diabetes, hormonal changes, and wearing tight, non-breathable clothing—a particular consideration in Hong Kong's subtropical climate.
Common Symptoms in Women
Candidiasis frequently affects women, with vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), or a vaginal yeast infection, being one of the most common forms1.
.jpg)
Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Vaginal Yeast Infection)
The symptoms are primarily localised to the vulva and vagina and can range from mild to severe:
- Intense Itching and Irritation: This is often the most prominent and bothersome symptom, causing significant discomfort2.
- Burning Sensation: A feeling of burning, especially during urination (external dysuria) or intercourse, is very common2.
- Abnormal Discharge: The classic sign is a thick, white, "cottage cheese" or "bean curd" like discharge that is typically odourless2. It's important to note that not all women with VVC have this discharge, and its absence doesn't rule out an infection.
- Redness and Swelling: The vulva and vaginal tissues often appear red, swollen, and inflamed2. Sometimes, small fissures or cracks in the skin can develop due to irritation.
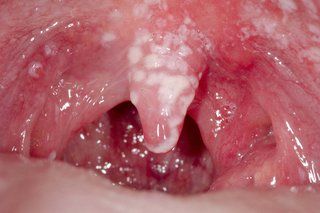
Other Forms Affecting Women
Women can also experience candidiasis in other areas, with symptoms similar to those that may appear in men:
Oral Thrush: Creamy white, slightly raised lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, or throat that can be painful and may bleed when scraped.
 candidiasis.jpg)
Skin (Cutaneous) Candidiasis: Appears in moist skin folds (under breasts, groin, armpits). It presents as a red, raw rash with clearly defined edges, often accompanied by itching or burning. Small pus-filled pimples may appear around the main rash.
Common Symptoms in Men
While less frequently discussed, men can certainly develop candidiasis, often in the following forms:
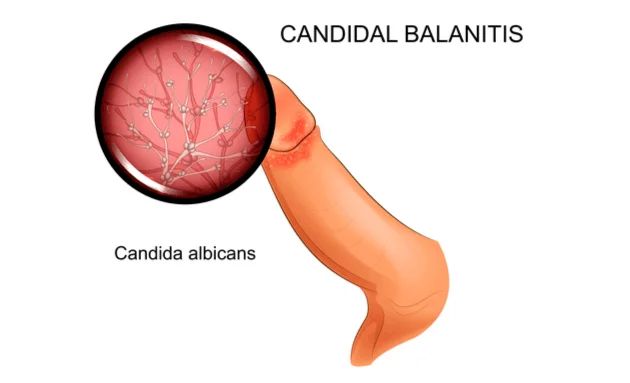
Penile Candidiasis (Balanitis)
This infection affects the head of the penis (glans) and, if present, the foreskin.
- Redness and Rash: The glans becomes red, inflamed, and may develop a spotted rash.
- Itching and Burning: Significant itching and a burning sensation on the penis are common complaints.
- Discharge: There may be a thick, lumpy discharge under the foreskin, sometimes with an unpleasant smell.
- Discomfort: Pain during sexual intercourse or urination can occur.
Other Forms Affecting Men
Men are equally susceptible to the non-genital forms of candidiasis:
- Oral Thrush: Symptoms are identical to those in women.
- Skin (Cutaneous) Candidiasis: Symptoms are identical to those in women, commonly occurring in the groin area.
Differentiating Candidiasis from Other Conditions
It's easy to confuse the symptoms of candidiasis with other common infections. The following table outlines the key differences:
| Condition | Primary Cause | Key Differentiating Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Vulvovaginal Candidiasis | Fungal (Candida overgrowth) | Intense itching, thick white odourless discharge, redness, burning. |
| Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) | Bacterial imbalance | Thin, grey/white discharge with a strong "fishy" odour, especially after sex. Itching is less prominent. |
| Trichomoniasis | Parasite (STI) | Frothy, yellow-green discharge, often with a foul odour. May cause painful urination. |
| Penile Candidiasis | Fungal (Candida overgrowth) | Red, itchy rash on glans, possible thick discharge under foreskin. |
| Balantis (other causes) | Bacterial, irritant, skin condition | Similar redness, but often without classic "cottage cheese" discharge. May be linked to poor hygiene or specific dermatoses. |
Crucial Point: One study found that among women visiting a clinic with symptoms like increased discharge or itching, only 28% actually had candidiasis, while over 50% had other conditions like BV or STIs1. This highlights why accurate diagnosis is essential.
When to See a Doctor in Hong Kong
You should consider seeking professional medical advice if:
- You are experiencing these symptoms for the first time.
- Symptoms are severe or do not improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- Infections recur frequently (four or more times a year).
- You are pregnant, have a weakened immune system, or have uncontrolled diabetes.
- You are unsure of the diagnosis, as symptoms between different vaginal or penile conditions can overlap.
In Hong Kong, you can consult a general practitioner, dermatologist, gynaecologist, or urologist. The Department of Health's Social Hygiene Clinics also provide confidential consultation, testing, and treatment services for sexually transmitted infections, which include diagnosing genital candidiasis.
Suggested Full Candidiasis Screening
Key Takeaways
Candidiasis is a manageable condition. The most telling symptoms for women are severe vulvar itching, burning, and a thick, odourless discharge. For men, redness, itching, and a rash on the head of the penis are key signs. Given Hong Kong's climate, being mindful of keeping skin dry and breathable is a good preventive step. If in doubt, always err on the side of caution and get a professional diagnosis to ensure you receive the correct and most effective treatment.
Ref:
11/F, 168 Queen’s Road Central, Central
(7 min from Central MTR Exit D2 /
2 min from Sheung Wan MTR Exit E2)
Hourly Parking Nearby : The Center, Grand Millennium Plaza
Mon-Fri : 9:45a.m. – 1:45p.m. ;
3:00p.m. – 6:10p.m.
Sat : 9:45a.m. – 1:15p.m.
Sun and Public Holiday: Close
By Appointment Only

