Balanitis, Symptoms & Treatments
Balanitis refers to acute or chronic skin inflammation of the glans (the head of the penis), commonly seen in uncircumcised men. While it is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection (STI), it can be triggered by sexual activity. If left untreated, the inflammation may spread to the urethra, causing urethritis, and even affect sexual function. Studies show that approximately 3-11% of men experience balanitis at least once in their lifetime[1], with diabetic patients having a threefold higher risk[2].
Causes of Balanitis
The inflammation is often caused by bacterial, fungal, or other pathogenic infections on the glans. However, chemical irritants can also lead to balanitis. If there is any damage to the penis, the risk of infection increases.
- Infection due to sexual activity
- Friction-induced injury
- Allergic reaction from contact with clothing
- Irritants, such as medications, urine, smegma, soap, or spermicides
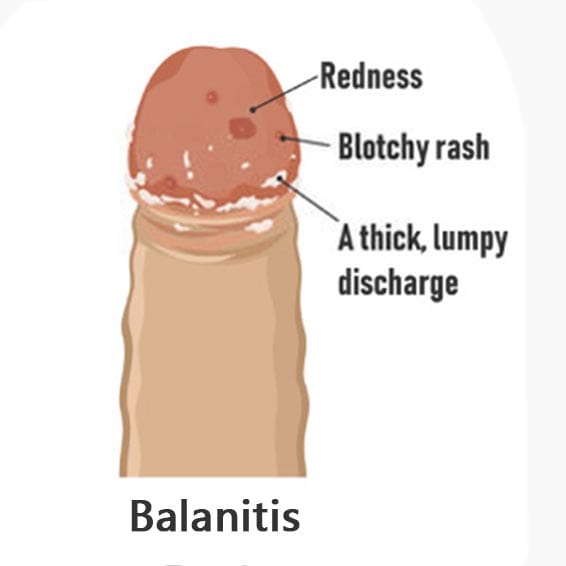
Symptoms of Balanitis: Peeling, Itching, Pain, Red Spots
- Common symptoms affecting the penis or foreskin include:
- Redness (erythema) on the penis or foreskin
- Rashes on the glans or foreskin
- Peeling skin
- White spots
- Pain or itching on the glans
- Foul-smelling discharge from infected skin
- Difficulty retracting the foreskin (due to swelling or scabbing)
- Pain during urination or stinging at the urethral opening
- White/yellow discharge (infectious) or clear fluid (allergic)
5 Major Types of Balanitis
Balanitis can be classified into five types based on the causative bacteria, fungi, pathogens, or irritants.
1. Infectious Balanitis
- Candidal Balanitis: The most common type (63% of cases[3]), caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans. More likely in moist environments (e.g., poor hygiene in uncircumcised men) or poorly controlled diabetes.
- Bacterial Balanitis: Primarily caused by Streptococcus (42%) and Staphylococcus aureus (28%)[4], often occurring after sexual activity or in immunocompromised individuals. Other bacteria like Gardnerella, Lactobacillus, and Atopobium may also be involved.
- STI-related Balanitis: Caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV), gonorrhea, chlamydia, or syphilis, often accompanied by urethral discharge and ulcers.
2. Contact Balanitis
- Chemical irritation: Allergic reactions to soaps, shower gels, spermicides, or low-quality condom lubricants.
- Friction-induced: Excessive washing or sexual activity causing micro-tears, leading to inflammation (often acute superficial balanitis).
3. Balanitis Xerotica Obliterans
- Chronic inflammation causing thinning and dry scaling of the glans skin, typically seen in older men, possibly linked to hormonal changes or autoimmune disorders.
4. Circinate Balanitis
- Characterized by ring-shaped red patches or ulcers, sometimes associated with Reiter’s syndrome or systemic diseases.
5. Recurrent Balanitis
- Recurring episodes (≥3 times/year), mainly due to:
- Untreated infections (e.g., untreated partner with candidiasis).
- Poorly controlled diabetes.
- Long foreskin with hygiene difficulties.
Treatment for Balanitis
Can balanitis resolve on its own?
In cases involving high-risk sexual behavior, symptoms are unlikely to subside without intervention and may worsen, causing further damage. Therefore, treatment should be sought based on symptom severity.
Mild cases: Slight redness, itching, or odor may improve with daily gentle cleansing using water.
Severe cases: If symptoms like erythema, foul odor, ulcers, bleeding, or discharge occur, prompt medical attention is necessary for diagnosis and targeted treatment.
Doctors may prescribe topical or oral antibiotics based on the underlying cause. Testing may be conducted to ensure precise medication selection, improving efficacy and reducing unnecessary discomfort.
Prevention of Balanitis
Maintain penile hygiene; avoid harsh soaps.
Circumcision can reduce recurrent balanitis.
In-Depth Analysis: Candidal Balanitis
The incidence of male candidal balanitis is rising, primarily due to:
Sexual contact: Men who have intercourse with women suffering from candidal vaginitis have a 69.4% infection rate.
Indirect contact: Shared towels, underwear, or baths can spread infection, especially in uncircumcised men where Candida thrives under the foreskin.
Symptoms of Candidal Balanitis:
- Mild redness and dryness on the glans and foreskin.
- White, cheese-like patches on the inner foreskin and coronal sulcus.
- If the scrotum is infected, scaly red rashes with intense itching may appear.
- Urinary frequency/urgency if the urethra is affected.
Severe cases may involve foreskin swelling, ulcers, or chronic fissures/fibrosis.
Treatment usually involves antifungal creams, with oral antifungals for severe cases.
8 Key Home Care & Prevention Tips
1 .Daily hygiene: Gently rinse the foreskin with warm water (avoid soap).
2. Dry thoroughly after washing to prevent moisture buildup.
3. Safe sex: Use fragrance-free condoms; urinate post-intercourse.
4. Avoid irritants: Skip alcohol-based wipes, perfumes, or harsh lubricants.
5. Diabetes control: Keep HbA1c <7% to reduce Candida growth.
6. Clothing choice: Wear breathable cotton underwear; avoid tight pants.
7. Partner treatment: If infectious, ensure your partner gets tested/treated.
8. Boost immunity: Take vitamin C/D[5] and zinc; exercise re
gularly.
Q&A on Balanitis
Q1: Can balanitis spread via toilet seats or towels?
➜ Very unlikely! Candida/bacteria require direct contact, but sharing towels may pose a slight risk.
Q2: Can saltwater or iodine help?
➜ Misconception! Saltwater may irritate wounds, and iodine (if used) must be diluted 10x and applied only to unbroken skin. Overuse disrupts natural flora.
Q3: Is masturbation/sex safe during treatment?
➜ Avoid! Friction worsens inflammation, and infectious balanitis may transmit to partners.
[1-5]: Citations from medical literature (retained as references).
(Note: Some technical terms like Candida albicans and Reiter’
s syndrome are kept in original form for accuracy.)
[1] Balanitis. Anton A. Wray; James Velasquez; Stephen W. Leslie; Shailesh Khetarpal.
[2] American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2023;46(Suppl 1):S103-S115. doi:10.2337/dc23-S007
[3] Patel G, et al. BMJ. 2022;377:e068435. doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068435
[4] Edwards SK, Bunker CB. Bacterial balanitis: microbiological spectrum and antibiotic resistance patterns. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021;34(4):e0002321. doi:10.1128/CMR.00023-21
[5] Martens PJ, Gysemans C. Vitamin D's effect on immune function. Nutrients. 2023;15(2):384. doi:10.3390/nu15020384
Balanitis
Balanitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the skin caused by the glans (head of the penis), commonly seen in uncircumcised men. Balanitis is not a sexually transmitted disease, but it can be caused by sexual activity.
Causes of Balanitis
Balanitis is often caused by bacterial, fungal or other pathogenic infection of the head of the penis. However, the irritation of the glans skin by chemicals can also lead to balanitis. If the penis has wound, it is more likely to be infected and cause balanitis.
- Infection due to sexual activity
- friction trauma
- Allergies from contact with clothing
- Irritants such as: drugs, urine, smegma, soap, spermicide, etc.
Symptoms of Balanitis
Common balanitis symptoms can appear on the penis or foreskin:
- Redness of the penis or foreskin (erythema)
- rash on the glans or foreskin
- sore or itchy glans
- Foul-smelling discharge from infected skin
Types of Balanitis
It can be classified by bacteria, molds or pathogens that cause balanitis
- Acute superficial balanitis (caused by trauma)
- Bacterial balanitis (Lactobacillus, Atopoiella, etc.)
- candidal balanitis
- Trichomonas balanitis
- Chlamydia balanitis
- HPV balanitis
- Syphilis balanitis, etc.
Balanitis treatment
Doctors treat different causes of infections with different medicines, which may include some topical or oral antibiotics. In many cases, balanitis examinations are carried out so that targeted drugs can be used, which greatly improves the treatment effect and reduces unnecessary pain.
Ways to prevent balanitis
Pay attention to the cleaning of the penis and avoid using harsh soaps Circumcision to reduce recurrent inflammation of the glans
Candidal Balanitis
The incidence of male candidal balanitis is increasing, and the main reason is related to sexual contact. Anyone who has sexual intercourse with women suffering from candidal vaginitis is easily infected; secondly, contact with indirect objects, such as other people's underwear and bath towels , baths, etc., plus if the foreskin is too long, Candida proliferates in the inner plate of the foreskin, the coronal sulcus and the glans.
It has been found that 69.4% of men who have sexual contact with patients with candida vaginitis have genital infections, and those with candida vaginitis have 4 times the detection rate of candida on the penis of their husbands than those without vaginitis.
Symptoms of candidal balanitis
- Mild flushing, dryness and smoothness of the foreskin and glans of the penis
- White cheese-like patches on the inner plate of the foreskin and the coronal sulcus of the glans
- If the scrotum is infected, a scaly erythematous rash may be seen on the contact surface with the penis, with obvious itching
- If the urethra is infected, frequent urination and urgency may occur.
- In a small number of patients, the foreskin edema is obviously accompanied by itching, and small ulcers may appear
Repeated episodes of candidal balanitis can cause local changes such as dry cracks and fibrosis. The treatment of the disease is generally topical antifungal ointment, or oral antifungal drugs in severe cases.
(Text Only)

