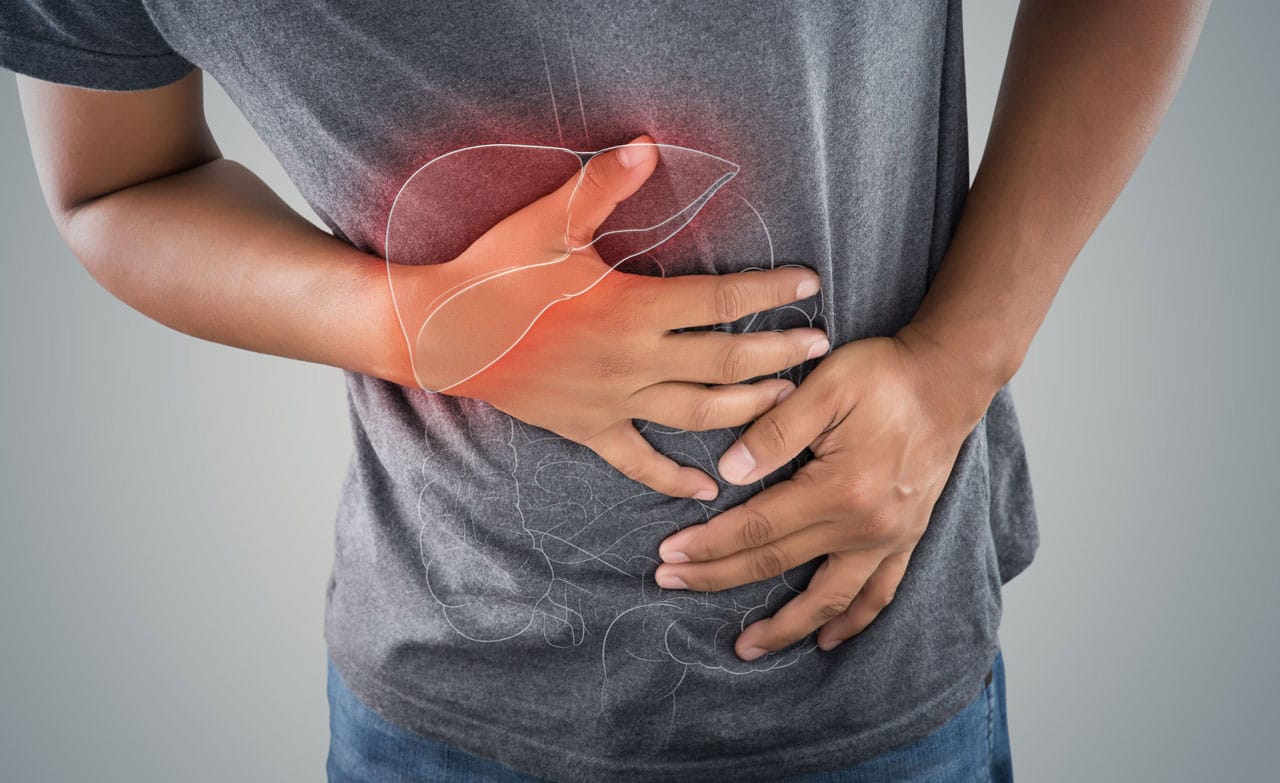
Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis refers to the inflammation of the liver that caused by viral infection. There are 5 types of hepatitis, and the most prevalent types of hepatitis are hepatitis A, B and C.
Hepatitis A infection is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV). HAV replicates in the liver cells and is present in the blood and feces. Hepatitis A infections are always acute and never result in chronic infection.
Hepatitis B infection is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV replicates within liver cells and is found in blood, semen, vaginal fluid and saliva. Hepatitis B infection can be acute or chronic, and the chance of chronic infection is inversely correlated with age of infection, with 90% infants, 30% children below 5 years of age and only 2-6% of adults becoming chronically infected. People with chronic hepatitis B infection are 15-25% more likely to develop liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hepatitis C infection is caused by the virus hepatitis C virus (HCV). HCV can cause both acute and chronic infections. Chronic hepatitis C carriers are more likely to develop liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
11/F, 168 Queen’s Road Central, Central
(7 min from Central MTR Exit D2 /
2 min from Sheung Wan MTR Exit E2)
Hourly Parking Nearby : The Center, Grand Millennium Plaza
Mon-Fri : 9:45a.m. – 1:45p.m. ;
3:00p.m. – 6:10p.m.
Sat : 9:45a.m. – 1:15p.m.
Sun and Public Holiday: Close
By Appointment Only

