Gonorrhea Symptoms in Men & Women: Hong Kong Complete Guide
Understanding Gonorrhea in Hong Kong
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. According to Hong Kong's Department of Health, STIs including gonorrhea have shown fluctuating trends in recent years, with young adults aged 20-29 being most affected. The infection can affect the genitals, rectum, and throat, and many infected individuals experience no symptoms, making regular testing crucial for sexually active people in Hong Kong.
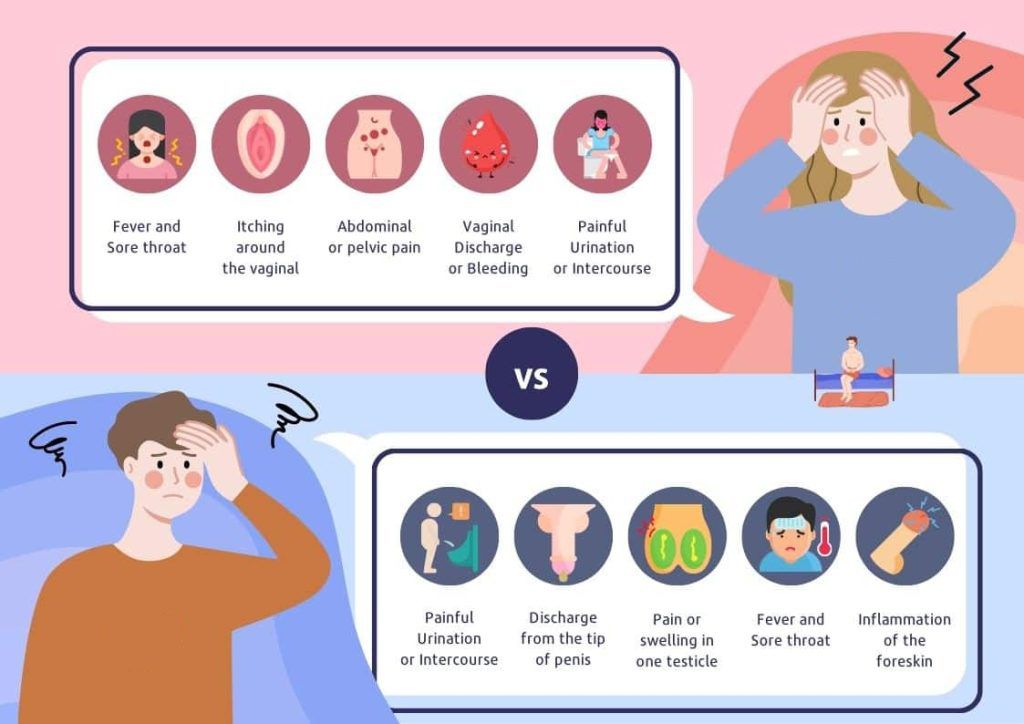
Common Gonorrhea Symptoms
Many people will not show any symptoms after being infected with gonococcus, and the symptoms of gonorrhea infection and non-gonococcal infection are very similar. There are two main symptoms of gonorrhea infection:
- Yellow-green or white discharge
- Burning when urinating
The symptoms of yellow and green discharge is very typical for genital gonococcus infection. However, gonorrhea can also infect anal and oral area.
Symptoms in Men
- Burning sensation during urination
- White, yellow, or green discharge from the penis
- Painful or swollen testicles (less common)
- Rectal discomfort, discharge, or bleeding (if infected through anal sex)
- Sore throat (if infected through oral sex)
Symptoms in Women
- Increased vaginal discharge (often yellow or bloody)
- Pain or burning during urination
- Vaginal bleeding between periods
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Rectal symptoms (discomfort, discharge, or bleeding)
Asymptomatic Cases
Approximately 50% of women and 10% of men with gonorrhea experience no noticeable symptoms, which contributes to unintentional transmission and delayed treatment. if you suspect after sex exposure or experience any symptoms of gonorrhea, you should get gonorrhea tested and treated for gonorrhea immediately.
Complications of Untreated Gonorrhea
In Women
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) - Can lead to chronic pain and infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy - Life-threatening condition
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Infertility due to scarred fallopian tubes
In Men
- Epididymitis - Painful inflammation of the testicles
- Prostate inflammation
- Urethral scarring causing urinary problems
- Infertility (rare)
In Both Genders
- Disseminated gonococcal infection (spread to joints and other body parts)
- Increased HIV transmission risk
- Infections in other areas (eyes, throat, rectum)
Gonorrhea Symptoms of Rectal/Anal Infection
Both male and female can be infected by gonorrhea with rectal/anal area, it may cause
- pain in the rectum or anus
- abnormal discharge from the rectum or anus
- pain during bowel movement
- bleeding from the rectum or anus.3
Gonorrhea Symptoms of Oral Infection
- sore throat4
1. (REF. Ref. Harrison WO, Hooper MR, Wiesner PJ et al. A trial of minocycline given after exposure to prevent gonorrhea. N Engl J Med, 300(19), 1074–1078 (1979).
2. (REF. Platt R, Rice PA, McCormack WM. Risk of acquiring gonorrhea and prevalence of abnormal adnexal findings among women recently exposed to gonorrhea. JAMA, 250(23), 3205–3209 (1983)
3. (REF. Rectal Gonorrhea in Men: Diagnosis and Treatment. Denis 1980).
4. (REF. The treatment of pharyngeal gonorrhoea with a single oral dose of cefixime. Young, 2007)
(Text Only)

